What are the rosmarinic acid purification methods?
2024-12-12 09:32:03
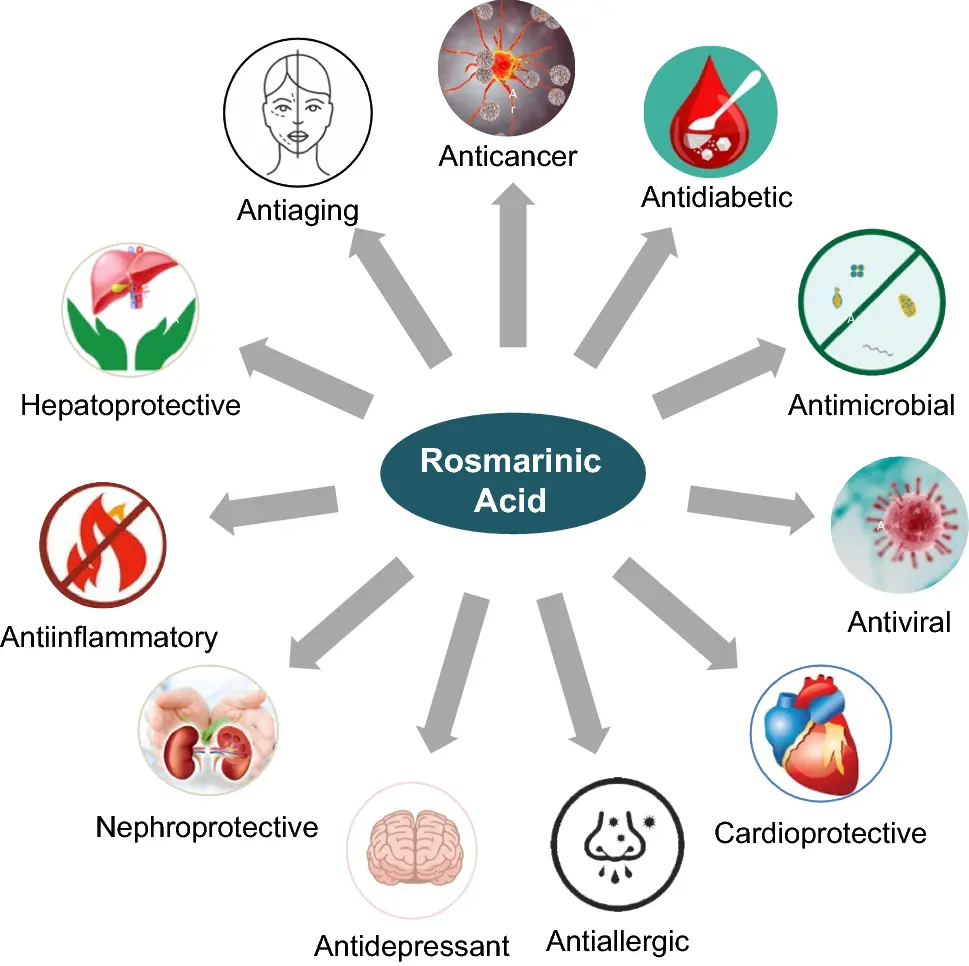
Rosmarinic acid is a natural polyphenolic compound widely found in various plants, such as rosemary, mint, and perilla. It is renowned for its powerful antioxidant activity and has significant applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries, often used as a natural preservative and an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial functional ingredient.

Kintai is a leading manufacturer and supplier in China's plant extract industry, and we can provide you with high-quality, high-purity rosmarinic acid. To fully realize the high value of rosmarinic acid, obtaining high-purity monomers is crucial. However, isolating and purifying rosmarinic acid from complex plant extracts is a challenge. Next, we will focus on commonly used rosmarinic acid purification methods to explore how to efficiently obtain high-purity products.
What is Rosmarinic Acid Used for?
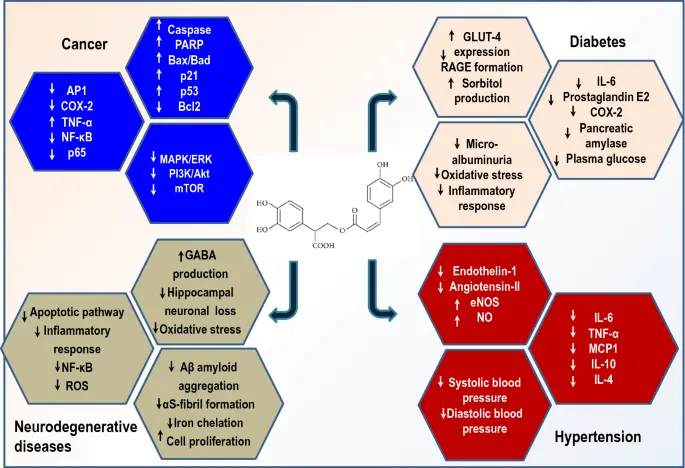
1. Exceptional Antioxidant Activity: This is the most fundamental and core function of rosmarinic acid. It effectively scavenge free radicals (such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS)) and inhibit lipid peroxidation. This mechanism enables it to:
- Protect cells: Reduce oxidative stress damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA, thereby delaying cellular aging.
- Applications in food and cosmetics: It can be used as a natural preservative in the food industry; in cosmetics, it helps with anti-aging and brightening skin tone.
2. Powerful Anti-inflammatory Effects: Rosmarinic acid can reduce the body's inflammatory response by inhibiting the production and release of key inflammatory factors (such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), etc.) and regulating classic inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-κB. This makes it show potential application value in alleviating inflammatory diseases such as arthritis and dermatitis.
3. Antibacterial and Antiviral Capabilities: Studies have shown that rosmarinic acid has certain inhibitory effects on various bacteria (such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli) and fungi. In addition, it also has antiviral activity against some enveloped viruses (such as herpesvirus and influenza virus), and its mechanism may be related to destroying the viral envelope or inhibiting the binding of the virus to the host cell.
High-purity rosmarinic acid purification methods
Obtaining high-purity rosmarinic acid from crude plant extracts requires efficient separation and purification techniques. Macroporous resin adsorption, column chromatography, and solvent extraction are three core methods, each with its own process flow and advantages and disadvantages.
1. Macroporous Resin Adsorption Method
- Process Flow: First, the aqueous extract of rosmarinic acid is passed through a pretreated macroporous resin column, where the target molecules are selectively adsorbed onto the resin. Then, unadsorbed water-soluble impurities such as sugars and proteins are washed away with a large amount of water. Next, a gradient elution is performed with ethanol solutions of increasing concentration; rosmarinic acid is usually desorbed in medium-concentration ethanol (e.g., 50%-70%). The eluent rich in rosmarinic acid is collected, concentrated, and dried to obtain a product with high purity.
- Advantages: Large adsorption capacity, low cost, simple operation, easy to scale up industrially, and the use of a water/ethanol system is safe and environmentally friendly.
- Disadvantages: Limited purity improvement (usually 50%-80%), poor separation effect for structurally very similar isomers.
2. Column Chromatography
- Process Flow: This method uses silica gel or polyamide as the stationary phase packed in a glass column. Crude rosmarinic acid is dissolved and loaded onto the sample, then eluted under normal or low pressure using a carefully formulated organic solvent system (such as chloroform-methanol-formic acid). Different polarities of components migrate at different rates in the column, thus achieving separation. Thin-layer chromatography monitoring is used to collect the eluent fractions, combine the target fractions, and recover the solvent to obtain high-purity rosmarinic acid. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) offers even higher separation efficiency and purity.
- Advantages: Strong separation efficiency, yielding monomers with over 95% purity, making it the preferred choice for standard preparation.
- Disadvantages: Small throughput, high solvent consumption, expensive equipment, high operating costs, and difficulty in directly applying to large-scale production.

3. Solvent Extraction Method
- Process Flow: This method utilizes the different partition coefficients of rosmarinic acid in two immiscible solvents for separation. Typically, the plant material is first extracted with water to obtain a crude extract. Then, multiple extractions are performed using organic solvents such as ethyl acetate or n-butanol, causing rosmarinic acid to transfer from the aqueous phase to the organic phase. By combining the organic phases and concentrating under reduced pressure to recover the solvent, the enriched rosmarinic acid extract can be obtained.
- Advantages: The equipment and operation are extremely simple; it can quickly remove most water-soluble impurities and achieve preliminary enrichment; it is often used as a pretreatment step for other purification methods.
- Disadvantages: The purification effect is limited, the product purity is not high, and the consumption of organic solvents is large, posing safety and environmental risks.
What is the dosage of Rosmarinic Acid Powder?
Understanding the appropriate dosage of rosmarinic acid powder is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic benefits while ensuring safety. The recommended dosage can vary significantly depending on various factors, including the specific condition being addressed, individual health status, and the form of supplementation being used.
Clinical studies have explored various dosage ranges, typically finding therapeutic effects at doses between 200-1000mg per day, divided into multiple doses. However, it's important to note that these dosages are often studied in specific contexts and may not be universally applicable. Some research has suggested that lower doses taken consistently over time may be more effective than larger acute doses, particularly for managing chronic conditions.
The bioavailability of rosmarinic acid is another crucial factor to consider when determining appropriate dosage levels. Studies have shown that the compound's absorption can be enhanced when taken with meals containing healthy fats, as rosmarinic acid is fat-soluble. This characteristic has led to recommendations for taking the supplement with meals to optimize absorption and effectiveness.
Timing of supplementation may also play a role in maximizing therapeutic benefits. Some research suggests that taking rosmarinic acid powder in divided doses throughout the day may be more effective than a single large dose, particularly for maintaining steady anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Morning and evening doses are commonly recommended to maintain consistent levels in the system.
Individual factors such as body weight, metabolism, and concurrent medications or supplements should also be considered when determining appropriate dosage levels. As with any therapeutic compound, it's advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it while monitoring response and tolerance.
For those specifically using rosmarinic acid powder for autoimmune conditions, working with a healthcare provider to determine the optimal dosage is crucial, as requirements may vary based on the specific condition and its severity. Regular monitoring and adjustment of dosage may be necessary to achieve optimal results while ensuring safety and effectiveness.
KINTAI High-purity Rosmarinic Acid
Healthkintai® is a leading manufacturer and supplier in the plant extraction industry, distinguished by our competitive advantages, which include a mature R&D team, a GMP-compliant factory, a large inventory, and complete certifications. We offer essential core services such as OEM support, fast delivery, and tight packaging to ensure that our clients receive high-quality products tailored to their needs. Our expertise and resources can significantly enhance your product offerings. For more details about rosmarinic acid, please feel free to contact us at health@kintaibio.com.

References:
1. Journal of Ethnopharmacology (2020): "Therapeutic potential of rosmarinic acid: A comprehensive review"
2. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy (2019): "Immunomodulatory effects of rosmarinic acid: A review"
3. Frontiers in Pharmacology (2021): "Rosmarinic Acid in Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review"
4. Natural Medicine Journal (2018): "Clinical Applications of Rosmarinic Acid in Immune Support"
5. Phytomedicine (2020): "Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of rosmarinic acid"
6. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2019): "Antioxidant Properties of Rosmarinic Acid"
7. International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2021): "Molecular Mechanisms of Rosmarinic Acid"
8. Current Pharmaceutical Design (2018): "Therapeutic Dosing of Rosmarinic Acid"
9. Nutrients (2020): "Safety and Efficacy of Rosmarinic Acid Supplementation"
10. Biochemical Pharmacology (2019): "Immunological Properties of Rosmarinic Acid"