Piperine vs Capsaicin
2026-02-03 16:49:00
In the global health ingredient market, piperine and capsaicin are popular ingredients in health supplements. One, derived from black pepper, possesses a surprisingly potent synergistic effect despite its mildness; the other, derived from chili peppers, contains targeted therapeutic power amidst its fiery intensity. Do you know their differences and applications? Healthkintai® is a manufacturer and supplier of piperine and capsaicin, offering products in various specifications. Please contact us at info@kintaibio.com.
What is Piperine/Capsaicin?
Piperine is the main bioactive alkaloid in black pepper (Piper nigrum L.), giving it its unique spicy flavor. It is primarily obtained from black peppercorns through solvent extraction. Its main benefits include significantly enhancing the bioavailability of other compounds (such as curcumin), earning it the title of "natural bio-enhancer"; possessing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; and promoting metabolism and energy expenditure. These properties make it highly valuable in dietary supplements, functional foods, and pharmaceuticals, especially in formulations requiring improved absorption efficiency.

Capsaicin is the key active ingredient in capsicum plants (such as chili peppers) that causes a pungent, burning sensation. It is mainly found in the placenta and pith of the fruit. It is primarily isolated and purified from dried chili peppers using organic solvent extraction methods (such as ethanol and acetone) or supercritical CO₂ extraction. Its main effects include: exerting significant local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects by consuming the neurotransmitter substance P, making it a core ingredient in topical analgesics; activating TRPV1 receptors to promote thermogenesis and fat oxidation, which is beneficial for weight management; and possessing properties that improve circulation and have antioxidant effects. These effects make it widely used in topical pharmaceuticals, health foods, and sports nutrition.

Key Differences between Piperine and Capsaicin
While both piperine and capsaicin are star alkaloids from spicy plants, they differ fundamentally in several dimensions.
- From a botanical perspective, piperine is extracted from black pepper (Piper nigrum), while capsaicin originates from plants in the Capsicum genus (such as red peppers). Their core chemical structures differ, determining their properties: piperine contains a piperidine ring, while capsaicin is based on a vanillin amide structure, directly affecting their interaction with human receptors.
- In terms of taste, piperine primarily delivers a sharp, lingering spiciness, while capsaicin provides a strong burning sensation, a hallmark of its activation of the TRPV1 receptor channel.
- Regarding the crucial aspects of absorption and bioavailability, piperine is renowned for its exceptional "bio-enhancing" ability, inhibiting metabolic enzymes in the liver and intestines and significantly improving the absorption of other co-administered active ingredients (such as curcumin); capsaicin itself does not possess this universal synergistic function.
- In the medical field, piperine is often taken orally to aid digestion, reduce inflammation, and act as an absorption enhancer; capsaicin, on the other hand, is primarily used topically as an analgesic, relieving muscle and joint pain and neurological discomfort by depleting neuropeptide P.
- Finally, in terms of spiciness, piperine typically provides only a mild to moderate spiciness, while capsaicin has a very wide range of intensity, ranging from a slight burning sensation to an unbearable, intense burning pain, depending on its purity and concentration.
Benefits of Piperine and Capsaicin
Piperine's core efficacy lies in its exceptional bioavailability enhancement. As a natural metabolic enzyme inhibitor, it significantly slows down the first-pass metabolism and metabolic rate of other active ingredients (such as curcumin, resveratrol, and various vitamins) in the liver and intestines, thereby greatly increasing their absorption rate and bioavailability, with enhancements reaching tens of times. Furthermore, piperine itself exhibits mild antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and promotes metabolism, playing an indispensable role as a synergist in dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals.
Capsaicin's efficacy is centered on its strong targeted action. It specifically activates and subsequently depletes substance P, the neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting pain, resulting in sustained and significant local analgesia and anti-inflammatory effects, making it a cornerstone ingredient in topical analgesics (such as patches and creams). Simultaneously, capsaicin activates thermogenic receptors, promoting energy expenditure and fat oxidation, aiding in weight management. Therefore, its applications primarily focus on functional products for pain management, exercise recovery, and metabolic enhancement, making it a typical "direct-acting" active ingredient.
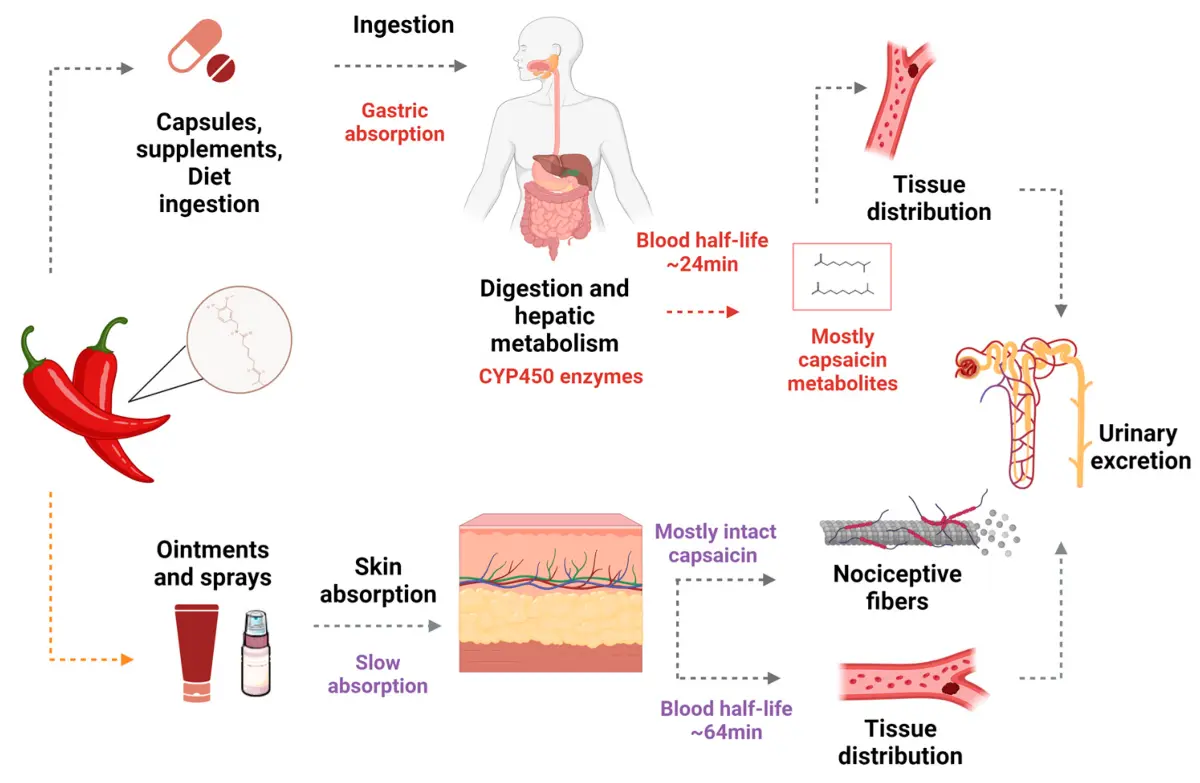
Is Piperine and Capsaicin safe?
Piperine and capsaicin exhibit significantly different safety profiles. Piperine, as an oral ingredient, is considered relatively safe at conventional doses (usually not exceeding 15 mg daily). Its main risk stems from its potent "bio-enhancing" effect—it may significantly increase the blood concentrations of co-administered drugs (such as certain cardiovascular medications and antiepileptic drugs), potentially leading to unknown interactions or adverse reactions. Therefore, strict drug compatibility assessment is necessary in formulation applications.
In contrast, the safety concerns regarding capsaicin focus on local reactions caused by topical application. Burning sensations, erythema, or itching are common upon initial use due to its activating effect on nerve endings, and tolerance usually develops with continued use. However, high concentrations or application to sensitive areas (such as mucous membranes or broken skin) may cause severe irritation or even chemical burns. Both require ensuring high purity of raw materials to avoid additional risks from impurities.

Where to buy the best Piperine and Capsaicin?
Choosing our piperine and capsaicin is a wise decision that ensures superior quality, reliable assurance, and a competitive edge. We provide pharmaceutical-grade, high-purity raw materials and strictly adhere to multiple international certification systems, including GMP, ISO, and HACCP, ensuring quality control throughout the entire process from raw material traceability to finished product delivery. More importantly, leveraging our vertically integrated supply chain and large-scale production advantages, we can offer truly competitive factory-direct prices while maintaining top-tier quality. Contact us at info@kintaibio.com.